Mechatronics Engineering
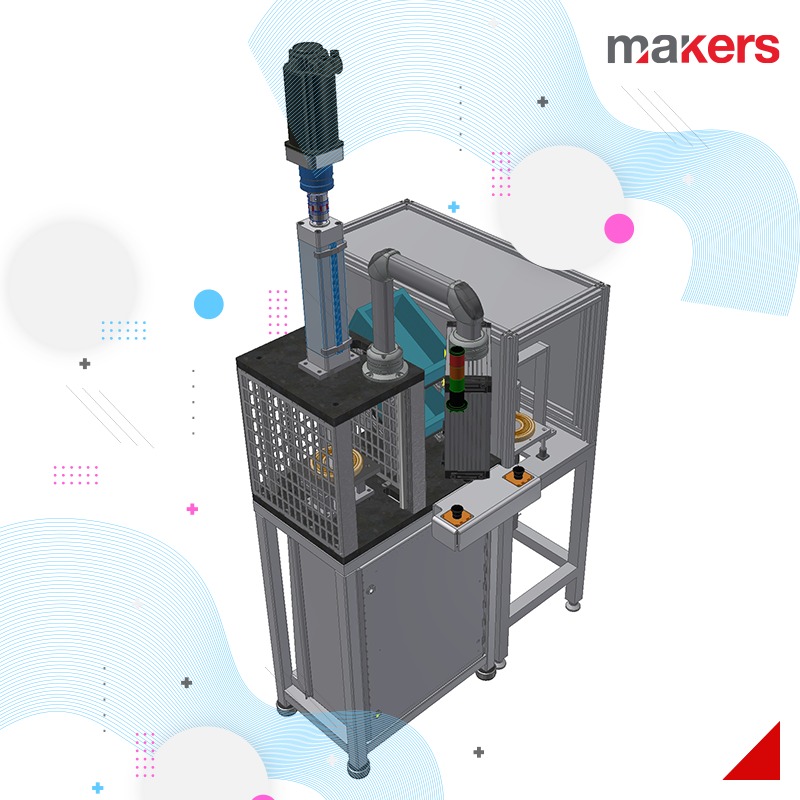
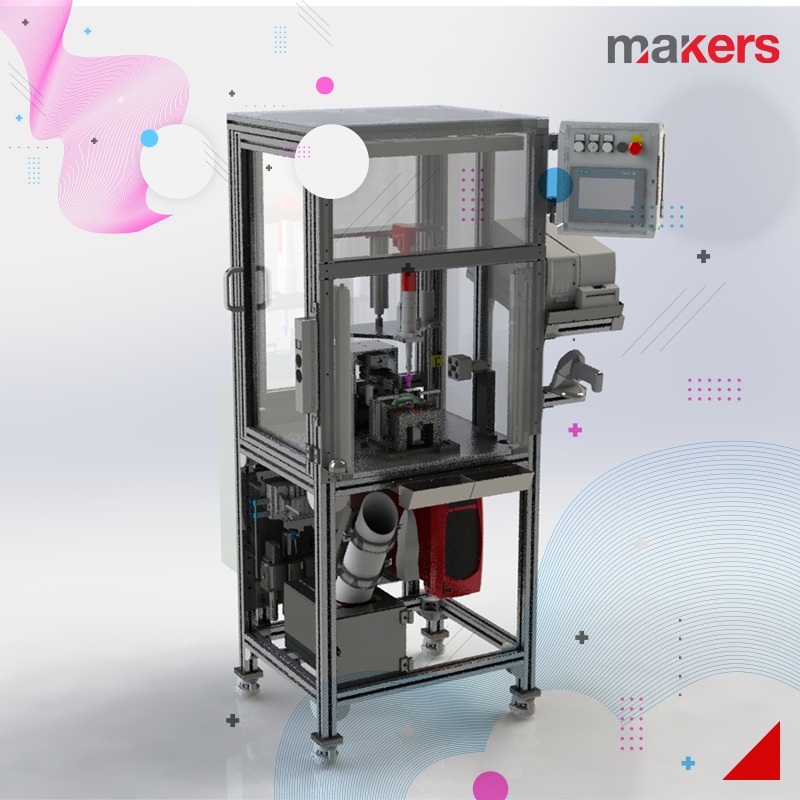
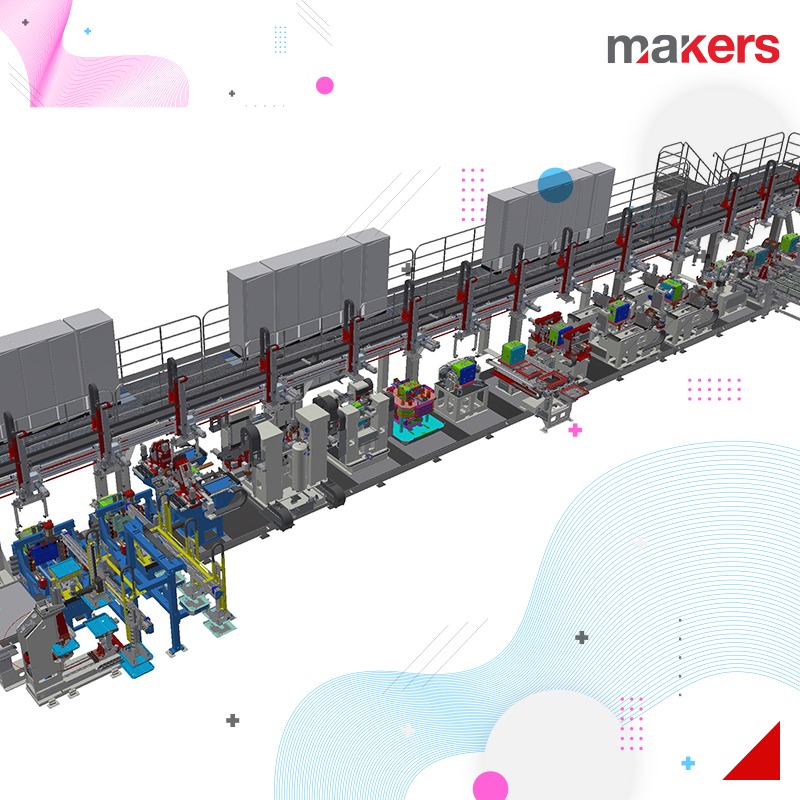
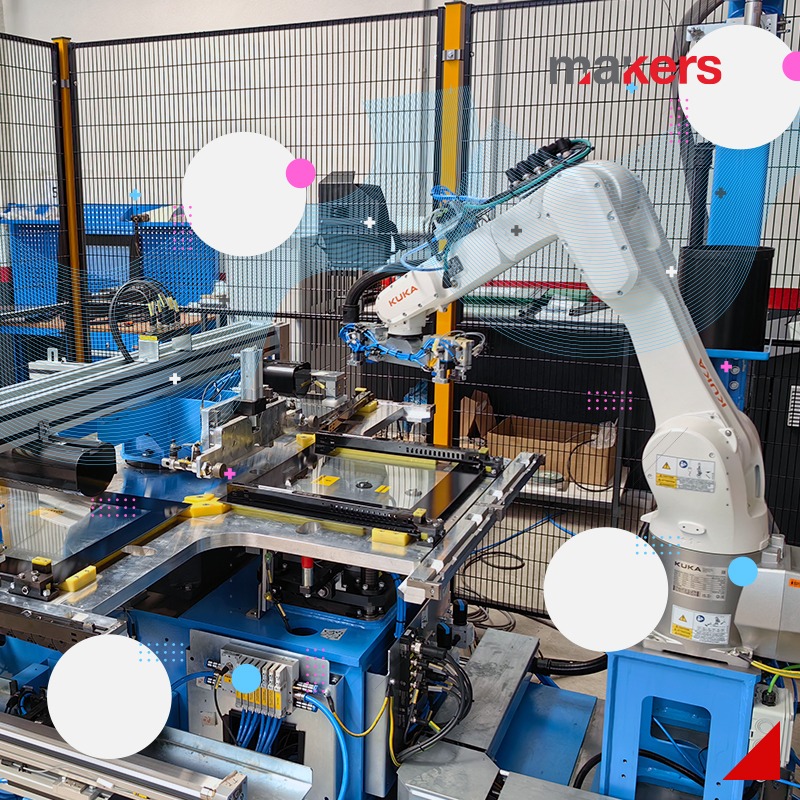
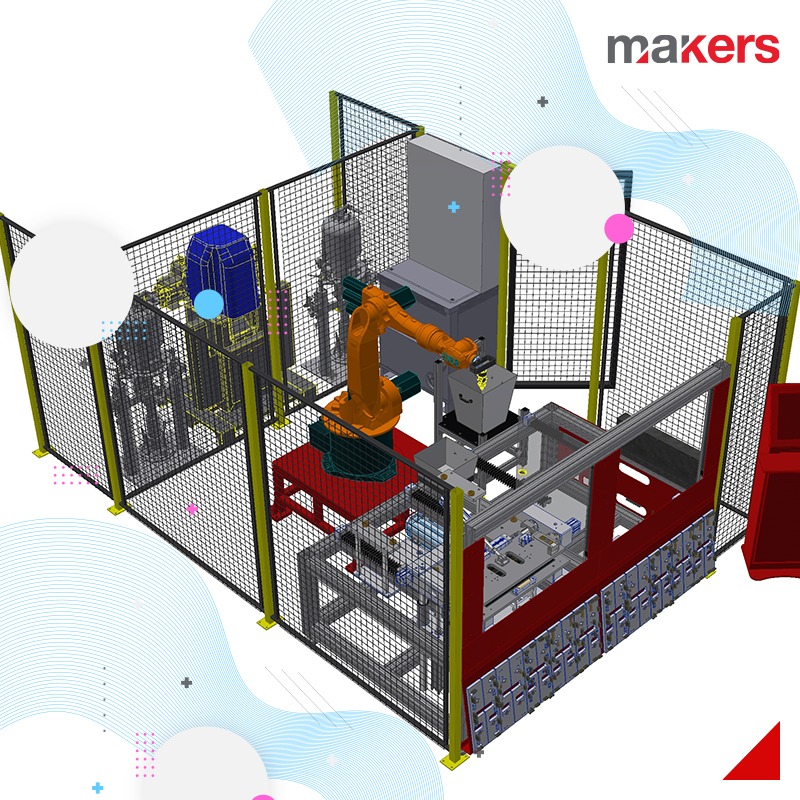
We frequently use 6-axis or Cartesian robot applications in the line installations we realize within the framework of factory automation. With our robotics team, which is especially competent in handling, palletizing, part feeding and bonding applications, we design and implement systems that we optimize with system simulations before manufacturing.
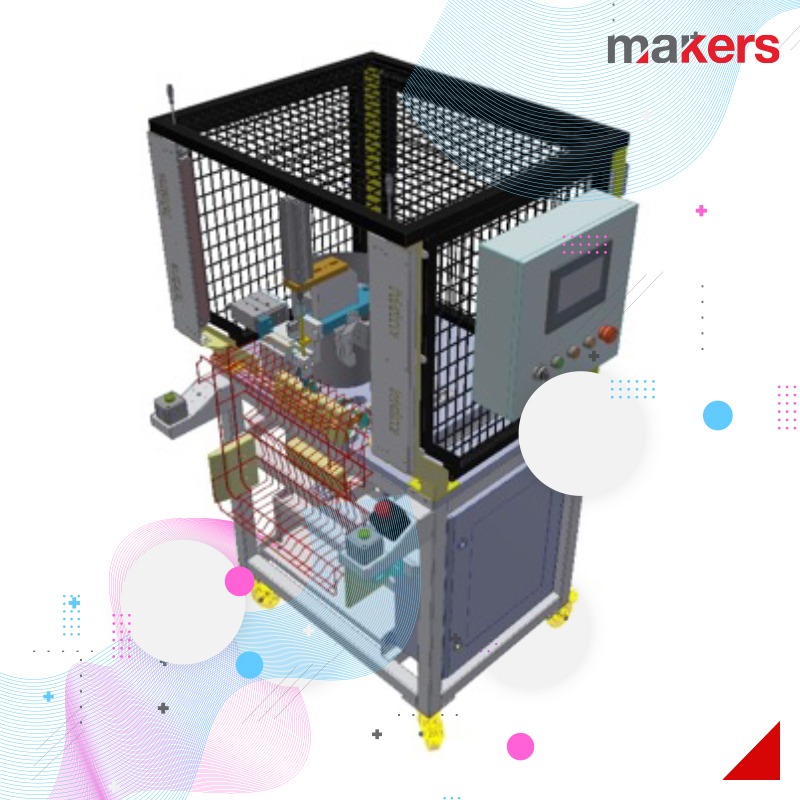
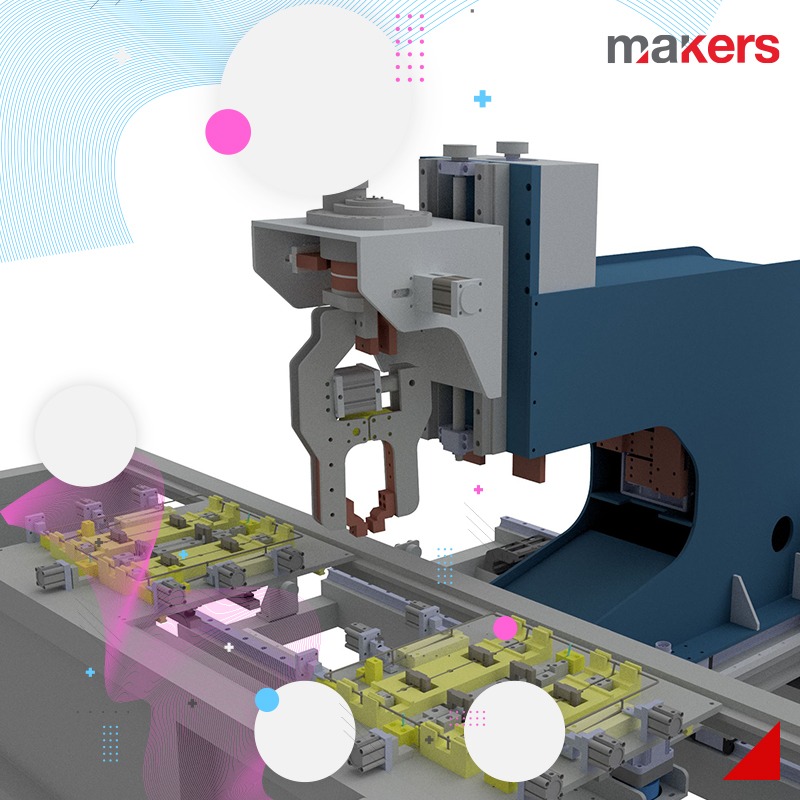
Cartesian systems: They can be designed to move in X-Y axes or X-Y-Z axes. Cartesian systems generally have linear motion and servo drive. Linear actuators used in the system can be in various forms according to the specific application. The drive system can be selected as belt, screw, rack and pinion, pneumatic.
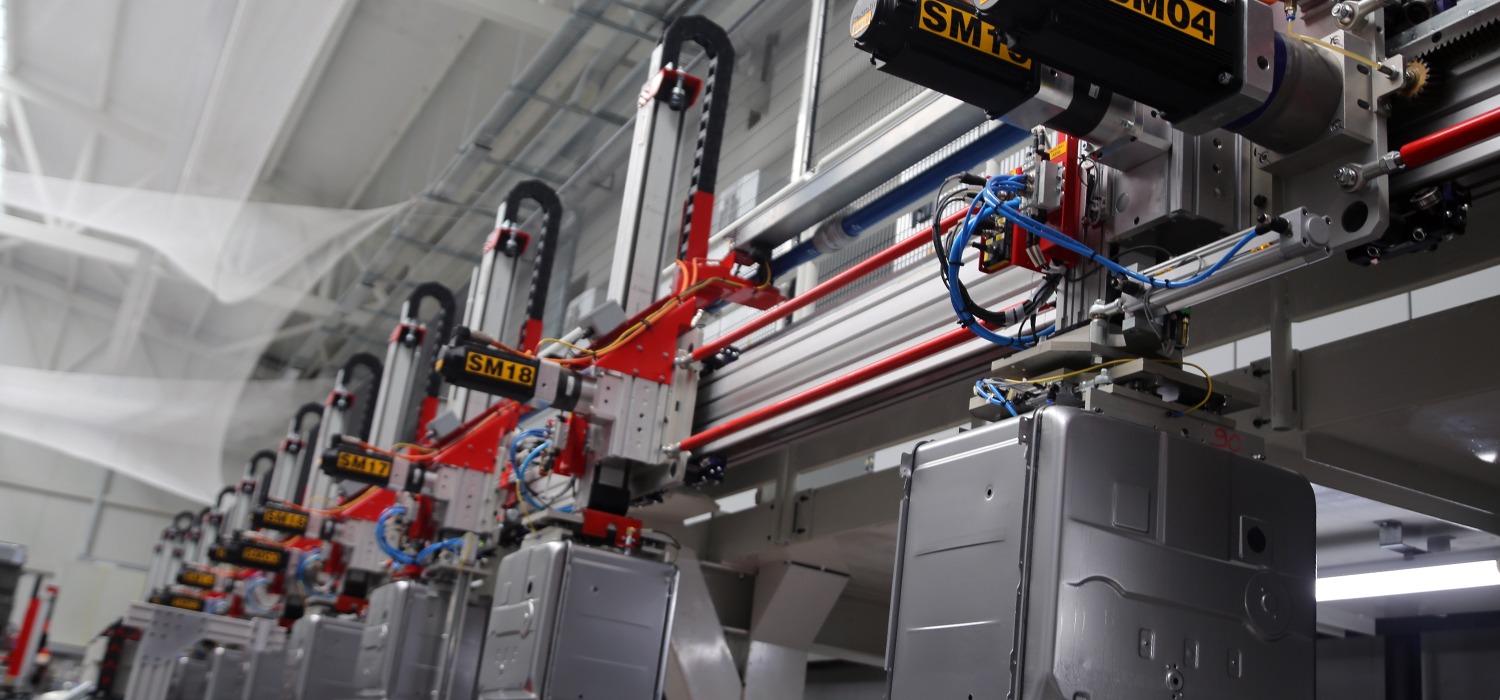

Cartesian systems have a higher payload capacity compared to their equivalent six-axis robots. This, combined with the lower cost and ease of programming for Cartesian systems, makes them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
With Cartesian systems, workspaces can be expanded by adding compatible modules to the existing mechanism. This modularity in Cartesian systems makes them much more versatile and capable of a longer lifespan in an industrial environment.
Cartesian systems also exhibit a high level of accuracy and precision compared to their rotary counterparts. This is because they only have linear motion and do not need to accommodate rotary motion. Cartesian systems can have tolerances in the micrometer (μm) range, while six-axis robots typically have tolerances in the millimeter (mm) range.